
What Are Liabilities in Accounting? (With Examples)
No one likes debt, but it’s an unavoidable part of running a small business. Accountants call the debts you record in your books “liabilities,” and knowing how to find and record them is an important part of bookkeeping and accounting.
Here’s everything you need to know about liabilities.
What are liabilities in accounting?
Liabilities are any debts your company has, whether it’s bank loans, mortgages, unpaid bills, IOUs, or any other sum of money that you owe someone else.
If you’ve promised to pay someone a sum of money in the future and haven’t paid them yet, that’s a liability.
How to find liabilities
You can find all of your liabilities on your company’s balance sheet, which is one of the three major financial statements. (The other two being the income statement and the cash flow statement.)
All balance sheets are divided into three sections:
The assets section, which tells you how much you have.
The equity section, which tells you how much you and other investors have invested in your business so far.
The liabilities section, which tells you what you owe.
Balance sheets used to be written out in two columns: the left column would be reserved for assets, while the right column was always reserved for liabilities and equity.
Here’s a balance sheet for a hypothetical business, Annie’s Pottery Palance, written out in this two-column format:
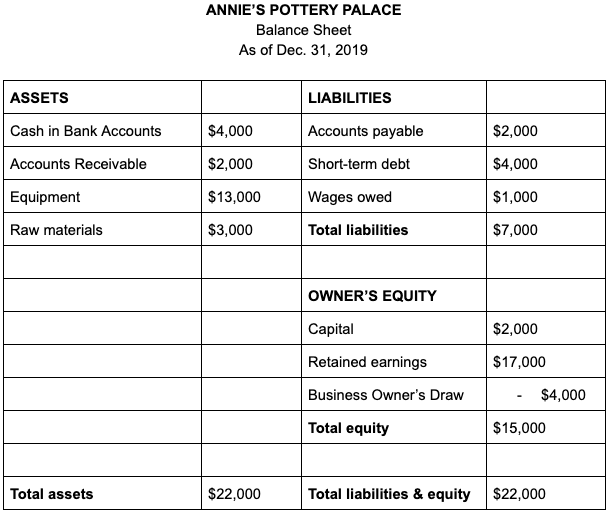
See how Annie’s total assets equal the sum of her liabilities and equity? That’s not just a fluke. If your books are up to date, your assets should also equal the sum of your liabilities and equity.
Accountants call this relationship the accounting equation, which is the most important equation in all of accounting. You can write it out in equation form like so:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
If your assets don’t equal your liabilities and equity, the two sides of your balance sheet won’t ‘balance,’ the accounting equation won’t work, and it probably means you’ve made a mistake somewhere in your accounting.
These days, the two-column balance sheet format is less popular. Your accounting software might spit out your balance sheet in a single-column, like so:
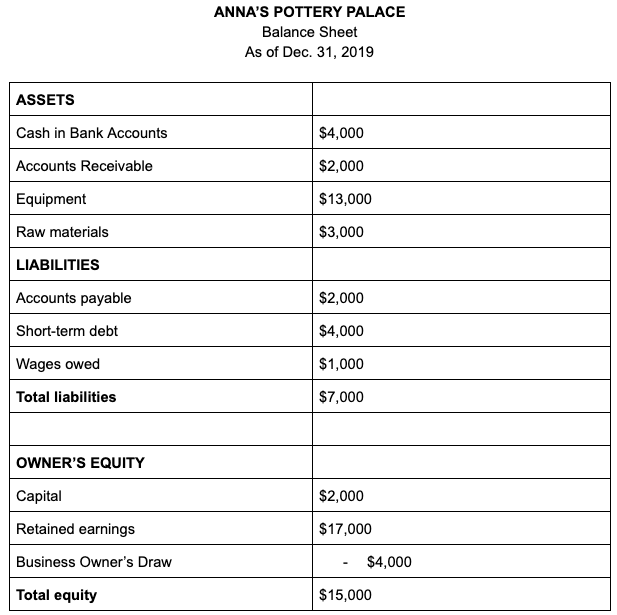
The important thing here is that if your numbers are all up to date, all of your liabilities should be listed neatly under your balance sheet’s “liabilities” section.
Further reading: What Are Assets, Liabilities, and Equity?

Get crystal clear financial statements every month.
Powerful financial reporting comes standard with Bench. Track every business transaction and performance metric like a pro, and run a smarter business right away.
Learn MoreExamples of liabilities
Most businesses will organize the liabilities on their balance sheet under two separate headings: current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
Current liabilities are debts that you have to pay back within the next 12 months.
Long-term liabilities are debts that aren’t due for more than 12 months.
We separate these for two reasons:
It makes it easier for anyone looking at your financial statements to figure out how liquid your business is (i.e. capable of paying its debts).
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require you to do so.
Current liabilities
These are any outstanding bill payments, payables, taxes, unearned revenue, short-term loans or any other kind of short-term financial obligation that your business must pay back within the next 12 months.
Some common examples of current liabilities include:
- Accounts payable, i.e. payments you owe your suppliers
- Principal and interest on a bank loan that is due within the next year
- Salaries and wages payable in the next year
- Notes payable that are due within one year
- Income taxes payable
- Mortgages payable
- Payroll taxes
Long-term liabilities
Also sometimes called “non-current liabilities,” these are any obligations, payables, loans and any other liabilities that are due more than 12 months from now.
Some common examples of long-term liabilities include:
- Principal and interest payments due more than a year from now
- Bonds, debentures and long-term loans
- Deferred tax liabilities
- Lease payments that aren’t due for more than a year
- Pension obligations
- Mortgage, equipment and other capital payments that aren’t due for more than a year
What about contingent liabilities?
Some businesses might record a third type of liability on their balance sheets: contingent liabilities. These are any liabilities you might owe someone, depending on the result of a lawsuit or if you have to pay your customers back to satisfy the terms of a warranty, for example.

Get crystal clear financial statements every month.
Powerful financial reporting comes standard with Bench. Track every business transaction and performance metric like a pro, and run a smarter business right away.
Learn MoreHow to calculate liabilities
Because most accounting these days is handled by software that automatically generates financial statements, rather than pen and paper, calculating your business’ liabilities is fairly straightforward. As long as you haven’t made any mistakes in your bookkeeping, your liabilities should all be waiting for you on your balance sheet. If you’re doing it manually, you’ll just add up every liability in your general ledger and total it on your balance sheet.
But there are other calculations that involve liabilities that you might perform—to analyze them and make sure your cash isn’t constantly tied up in paying off your debts. We call this credit accounting.
Here are some common calculations that accountants use in credit accounting, and why they’re important:
The debt ratio
By far the most important equation in credit accounting is the debt ratio. It compares your total liabilities to your total assets to tell you how leveraged—or, how burdened by debt—your business is.
The debt ratio equation is:
Debt ratio = Total liabilities / Total assets
So the debt ratio for Annie’s Pottery Palace (from the balance sheet example above) would be:
Debt ratio = $7,000 / $22,000 = 31.8%
Generally speaking, the lower the debt ratio for your business, the less leveraged it is and the more capable it is of paying off its debts. The higher it is, the more leveraged it is, and the more liability risk it has.
Although average debt ratios vary widely by industry, if you have a debt ratio of 40% or lower, you’re probably in the clear. If you have a debt ratio of 60% or higher, investors and lenders might see that as a sign that your business has too much debt.
The long-term debt ratio
This ratio is similar to the debt ratio, except for one difference: it leaves current liabilities out of the equation.
The long-term debt ratio equation is:
Long-term debt ratio = Long-term liabilities / Total assets
So a company with $4,000 in long-term liabilities and $20,000 in total assets would have a long-term debt ratio of:
Long-term debt ratio = $4,000 / $20,000
Long-term debt ratio = 20%
We use the long term debt ratio to figure out how much of your business is financed by long-term liabilities. Generally speaking, you want this number to go down over time. If it goes up, that might mean your business is relying more and more on debts to grow.
The debt to capital ratio
Another popular calculation that potential investors or lenders might perform while figuring out the health of your business is the debt to capital ratio.
The equation for the debt to capital ratio is:
Debt to capital ratio = Total liabilities / Total liabilities + Total equity
That means that the debt to capital ratio for Annie’s Pottery Palace would be:
Debt to capital ratio = $7,000 / $7,000 + $15,000
Debt to capital ratio = $7,000 / $22,000
Debt to capital ratio = 31.8%
In most cases, lenders and investors will use this ratio to compare your company to another company. A lower debt to capital ratio usually means that a company is a safer investment, whereas a higher ratio means it’s a riskier bet.

Get crystal clear financial statements every month.
Powerful financial reporting comes standard with Bench. Track every business transaction and performance metric like a pro, and run a smarter business right away.
Learn MoreWhat's Bench?
We're an online bookkeeping service powered by real humans. Bench gives you a dedicated bookkeeper supported by a team of knowledgeable small business experts. We’re here to take the guesswork out of running your own business—for good. Your bookkeeping team imports bank statements, categorizes transactions, and prepares financial statements every month. Get started with a free month of bookkeeping.
This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, business, or tax advice. Each person should consult his or her own attorney, business advisor, or tax advisor with respect to matters referenced in this post. Bench assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.
| YOU MAY ALSO LIKE |
The main difference between cash basis and accrual accounting is the timing of when revenue and expenses are recognized. Which is right for your business?

The general ledger is your “source of truth” in bookkeeping. Here’s a simple explanation of what it is, and how to use it in your business.
Knowing the difference between income statements and balance sheets, and the information they hold, is critical to your success in business.
Want a free month of bookkeeping?
Sign up for a trial of Bench. We’ll do one month of your bookkeeping and prepare a set of financial statements for you to keep. No pressure, no credit card required.


































































No comments:
Post a Comment